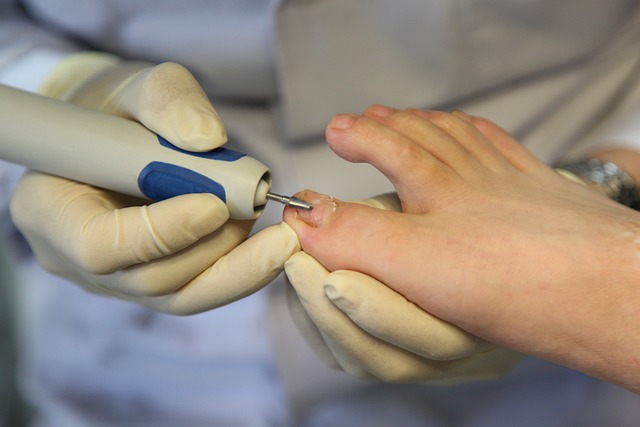
Breaking the Nail of the Matter: Understanding and Preventing Ingrown Toenails
- Genetics: If ingrown toenails run in the family, it may be due to inherited foot structure or nail shape. To prevent ingrown toenails, maintain good foot hygiene, avoid cutting nails too short, and choose shoes that fit well and don’t compress the toes.
- Improper nail trimming: Cutting the nails too short, round or at an angle can cause them to grow into the skin. To avoid this, cut straight across the nail and leave enough space to avoid the skin.
- Tight-fitting shoes: Shoes that are too tight can put pressure on the toes and cause the nails to grow into the skin. Choose shoes that fit well and leave enough room for the toes to move freely.
- Trauma to the toenail: Injuries or blunt force to the toenail can cause it to grow abnormally and into the skin. Avoid injuring the toenails and wear proper foot protection during physical activities.
- Fungal infections: Fungal infections can cause the toenail to become thick, brittle, and discolored, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails. Practice good foot hygiene and keep your feet dry to prevent fungal infections.
- Picking or digging at the toenail: Picking at the toenail can cause it to become damaged and increase the risk of ingrown toenails. Avoid picking at the toenails and keep them clean.
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating): Sweating can cause the skin to become soft and prone to infections, making it easier for the toenail to grow into the skin. Keep the feet dry and change socks regularly.
- Poor foot hygiene: Not washing the feet regularly, wearing the same shoes every day, and not changing socks can increase the risk of fungal infections and ingrown toenails. Keep the feet clean, dry and change socks daily.
- Nail deformities or irregularities: Nails that are abnormally shaped or curved are more likely to become ingrown. Consult a doctor if you have any concerns about the shape or appearance of your toenails.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing foot problems, including ingrown toenails. Keep your blood sugar levels under control, practice good foot hygiene, and consult a doctor regularly.
- Peripheral neuropathy: People with nerve damage in their feet are more susceptible to ingrown toenails. Consult a doctor for proper foot care and to prevent nerve damage.
- Poor circulation: Poor circulation can make it harder for the body to heal and prevent infections, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails. Exercise regularly, maintain a healthy diet, and quit smoking to improve circulation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Inflammation and joint pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis can make it difficult to care for the feet, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails. Consult a doctor for proper foot care and to manage symptoms.
- Gout: Gout can cause inflammation, joint pain, and toenail deformities, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails. Consult a doctor for proper treatment and to manage symptoms.
- Aging: As we age, our skin becomes thinner and less elastic, making it more susceptible to injuries and infections, including ingrown toenails. Keep the feet clean, dry, and well-cared for to prevent ingrown toenails. Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make the skin soft and more prone to injuries and infections, including ingrown toenails. Wear comfortable shoes, practice good foot hygiene, and avoid cutting the nails too short.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the feet and increases the risk of ingrown toenails. Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and wear shoes that fit well.
- Vitamin deficiency: A deficiency in certain vitamins, such as B-complex vitamins and vitamin D, can lead to brittle and deformed nails, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails. Eat a well-balanced diet and consider taking supplements if recommended by a doctor.
- Systemic diseases (such as psoriasis): Certain systemic diseases, such as psoriasis, can cause nail abnormalities and increase the risk of ingrown toenails. Consult a doctor for proper treatment and management of the underlying condition.
- Abnormal gait or walking patterns: Walking or standing for long periods, or having an abnormal gait, can cause excessive pressure on the toes and increase the risk of ingrown toenails. Consult a doctor for proper shoe recommendations and to address any gait issues.
Treatment for ingrown toenails typically involves lifting the affected portion of the nail and keeping it clean and dry. In some cases, a portion of the nail may need to be removed. If the condition is severe or recurrent, a doctor may recommend more extensive surgical treatment. It is always recommended to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.